Lung cancer is a serious medical condition in which abnormal cells grow uncontrollably in the tissues of the lungs. These abnormal cells form tumors that interfere with the normal function of the lungs, reducing the body’s ability to receive oxygen and remove carbon dioxide efficiently. Lung cancer is one of the most commonly diagnosed cancers worldwide and remains a leading cause of cancer-related deaths, largely due to late diagnosis and lack of early symptoms.
The lungs play a vital role in respiration, supplying oxygen to the bloodstream and supporting the function of every organ in the body. When cancer develops in lung tissue, it can affect breathing, energy levels, and overall health. Understanding lung cancer, its causes, symptoms, and progression is essential for early detection and effective treatment. In regions such as Thrissur, growing urbanization and environmental exposure have increased awareness about lung health and the importance of early evaluation for persistent respiratory symptoms.
How Lung Cancer Develops
Lung cancer begins when genetic changes occur in the cells lining the airways or lung tissue. These changes cause cells to grow uncontrollably instead of following the normal cycle of growth and death. Over time, these abnormal cells accumulate and form a tumor.
As the tumor grows, it may block air passages, invade surrounding tissues, or spread to nearby lymph nodes and distant organs through the bloodstream or lymphatic system. This ability to spread, known as metastasis, makes lung cancer particularly challenging to treat if not detected early.
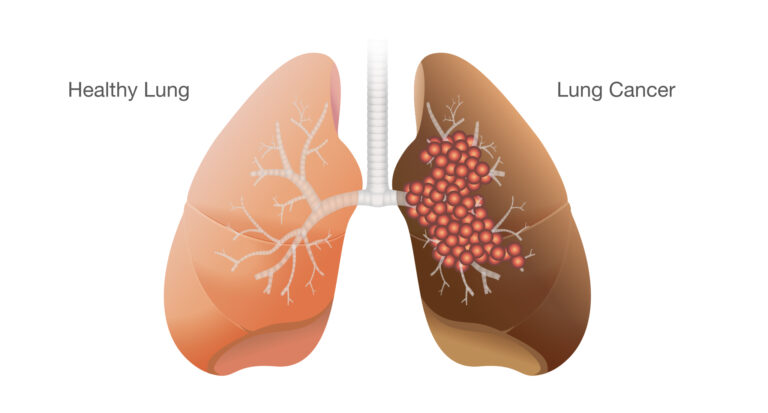
Types of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is broadly classified into two main types based on how the cancer cells appear under a microscope:
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
This is the most common type of lung cancer, accounting for the majority of cases. It generally grows and spreads more slowly than other forms. Subtypes include adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC)
This type is less common but more aggressive. It tends to grow rapidly and spread early to other parts of the body. Small cell lung cancer is often associated with smoking and requires prompt medical attention.
Why Lung Cancer Is Often Diagnosed Late
The lungs have a large reserve capacity, meaning they can continue to function even when part of the tissue is damaged. As a result, early tumors may not cause significant symptoms. Many patients seek medical attention only when symptoms become severe or interfere with daily activities.
Public health initiatives and improved access to medical care in areas like Thrissur have helped increase awareness, encouraging earlier screening and diagnosis for individuals at risk.
Stages of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is staged based on tumor size, lymph node involvement, and spread to other organs. Staging helps determine the extent of disease and guides treatment decisions.
Early-stage lung cancer is limited to the lungs
Locally advanced cancer involves nearby lymph nodes
Advanced-stage cancer has spread to distant organs
Earlier stages generally have better treatment outcomes, highlighting the importance of timely diagnosis.
Impact of Lung Cancer on Daily Life
Lung cancer can significantly affect physical, emotional, and social well-being. Breathing difficulties, fatigue, and pain may limit daily activities. Emotional challenges such as anxiety, fear, and stress are also common and require supportive care alongside medical treatment.
A comprehensive approach that addresses both physical symptoms and emotional health is essential for maintaining quality of life during treatment.
Public health initiatives and improved access to medical care in areas like Thrissur have helped increase awareness, encouraging earlier screening and diagnosis for individuals at risk. Regular health check-ups and prompt attention to symptoms are especially important for individuals with known risk factors.Understanding the causes, symptoms, and progression of lung cancer empowers individuals to seek timely medical care. Early detection and comprehensive management are key to improving survival and maintaining quality of life for those affected by lung cancer.
TABLE OF CONTENT
Candidate: Individuals diagnosed with lung cancer who are medically fit and whose condition can benefit from active therapy are considered good candidates for treatment. Learn more
Cost: The cost of lung cancer treatment varies based on cancer stage, treatment type, and duration of care required. Learn more
Consultation: During a lung cancer consultation, you can expect a detailed review of symptoms, diagnostic reports, and clear guidance on the next steps for evaluation and treatment planning. Learn more
Questions: Ask about the type and stage of lung cancer, available treatment options, expected benefits, possible side effects, and how treatment may affect daily life. Learn more
Risks: Risks can include fatigue, infection, breathing difficulties, nausea, hair loss, and treatment-specific complications depending on the method used. Learn more
Preparation: Preparation usually involves medical tests, medication review, lifestyle adjustments, nutritional support, and discussing practical and emotional support needs. Learn more
Steps: Lung cancer treatment typically follows a stepwise approach including diagnosis, staging, treatment planning, active therapy, and regular follow-up. Learn more
Recovery: Recovery may involve gradual improvement in strength, management of side effects, rehabilitation, and ongoing monitoring for treatment response. Learn more
Results: Results vary based on cancer stage and treatment type, ranging from symptom relief and disease control to long-term remission in some cases. Learn more
Before-and-after results: Before-and-after results may show reduced tumor size, improved breathing, better symptom control, and changes seen on follow-up scans. Learn more
Terms: Common terms include staging, metastasis, biopsy, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy. Learn more
Choosing the right doctor: Choosing the right doctor involves considering experience, specialization in lung cancer, access to multidisciplinary care, and clear communication. Learn more
